When the Cone Meets the Cloud: Cataract Surgery in Keratoconus
Scene 1 (0s)
When the Cone Meets the Cloud: Cataract Surgery in Keratoconus.
Scene 2 (14s)
No financial interest.
Scene 3 (22s)
Keratoconus. is a bilateral asymmetric non-inflammatory disorder characterized by progressive thinning and cone-shaped protrusion of the cornea leading to a decreased visual acuity and irregular astigmatism..
Scene 4 (33s)
Standard Amsler-Krumeich Keratoconus Classification.
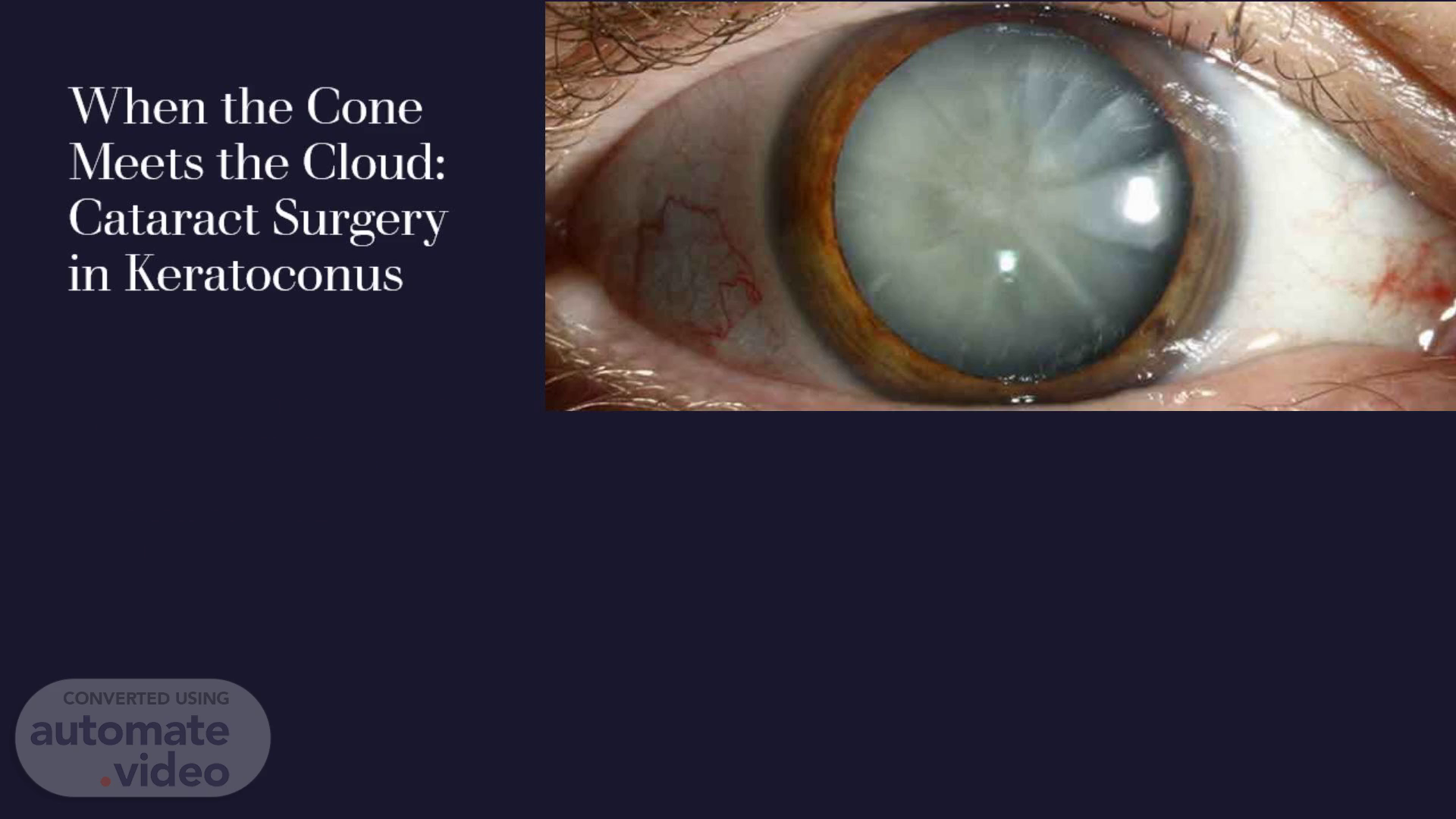
Scene 5 (54s)
Cataract in keratoconus. Lens spokes are common in KCN patients, and these are usually not visually significant. The most commonly identified type is the nuclear sclerosis type. However, many young patients with KCN may have steroid‑induced cataracts with posterior subcapsular opacification due to the chronic use of steroids for ocular allergy. The onset of cataract in KCN has also been reported to occur earlier than normal..
Scene 6 (1m 15s)
Challenges of cataract in KC. Preoperative challenges Intraoperative challenges Postoperative challenges.
Scene 7 (1m 22s)
Preoperative challenges. stability Biometry IOL.
Scene 8 (1m 29s)
Stability. Patients with stable, non-progressive KCN are ideal candidates. Less than 10% of eyes with KCN were found to progress after the age of 30 years CXL and intracorneal ring segments (ICRS) as an effective method to enhance corneal stability in mild to moderate KCN. recommended to calculate the IOL power at least 6 months after CXL The interval between ICRS and cataract surgery was 6 months. Patients with advanced KCN and a concomitant cataract may be good candidates for combined cataract surgery with tissue replacement (DALK,PKP) triple procedure or sequential procedure..
Scene 9 (1m 54s)
Iol calculation challenges in KC. - Irregular Tear Film: Keratoconic eyes often have unstable tear films - Fixation Difficulties: Patients with KCN may struggle to fixate properly - Limited Central Zone Analysis: Simulated keratometry values focusing solely on the central 3 mm zone may not accurately represent the overall corneal curvature in KCN -Steepened Corneal Surface: The steepening between the central cone and peripheral cornea can cause overestimation of K values - The apex of keratoconic corneas is off-center compared with the normal cornea, resulting in unreliability when measuring the visual axis. -Altered Corneal Ratios: The front-to-back corneal curvature ratios -Axial length (AL) measurement is equally important, as keratoconic eyes tend to be more myopic due to steeper corneal curvature and posterior segment elongation.
Scene 10 (2m 25s)
CL holiday. Soft CL 2 weeks. Soft toric lens 2wks. Hard /rigid lens 5wks or 1 mth for every decade. Scleral lens 5 days(less contact with cornea ).
Scene 11 (2m 37s)
IOL Biometry. No ideal formula (tendency toward hyperopic error) optical biometer-measured corneal powers were frequently higher than Pentacam. Pentacam demonstrated superior repeatability for keratometry <55 diopters Newer machines, such as IOLMaster 700 with TK (based on a swept source OCT), and elevation‑based devices, such as the Pentacam and Galilei, measure the posterior corneal curvature and are increasingly used in clinical practice.
Scene 12 (2m 57s)
Biometry formula KC specific formula Barrett True-K(MPC) Barrett True-K(PPC) Kane Keratoconus Normal formula Kane Barret universal II Haigis RBF EVO PEARL DGS SRK/T Hollady ll Hoffer Q Olsen.
Scene 13 (3m 9s)
Summary of predictive accuracy of IOL power calculation formulas in patients with keratoconus. A- Keratoconus-specific formulas..
Scene 14 (3m 46s)
Summary of predictive accuracy of IOL power calculation formulas in patients with keratoconus. B. Not Keratoconus-specific formulas..
Scene 15 (4m 19s)
IOL Biometry. BTK with PPC and MPC as preferred options for IOL power calculation in keratoconus patients. achieved 61.8% of eyes within ±0.50 D and 76.5% within ±1.00 D. Kane KCN demonstrated the second-highest overall accuracy after BTK, achieving 45.45% of eyes within ±0.50 D and 72.73% within ±1.00 D. RBF 3.0 formula shows higher percentage in predictive accuracy in comparing with other non-Keratoconus specific formula. SRK/T formula has tendency toward myopic prediction errors at higher corneal powers counterbalances the hyperopic tendency seen in patients with keratoconus . Barrett’s Universal II formula: less error in stage 1 and 2 but not used in stage 3.
Scene 16 (5m 6s)
No KC specific formula Stage 1 K<48 No adjustment of target refraction Stage 2 K<53 Myopic target(0.75-1.5) RBF 3.0,EVO2.0 Barret universal ll Kane SRK/T Stage 3 K<55 RBF3.0,EVO2.0 Barret universal ll Kane SRK/T Stage 4 K>55 Myopic target (2.0 – 3.0) RBF3.0,EVO2.0 Kane SRK/T Haigis Standard k(43.25) Myopic target(1.5-2.0) RBF3.0,EVO2.0 SRK/T Haigis.
Scene 17 (5m 40s)
Which IOL?. Monofocal and spherical aberration Toric iol ? Multifocal?.
Scene 18 (5m 48s)
Monofocals …spherical aberration. Most cornea has positive SA. IOL with –ve SA used in normal eye to improve visual quality. Keratoconic cornea has negative SA (similar to after hyperopic LASIK) Choose lens with neutral or +Ve SA No implantation of IOL with –Ve SA.
Scene 19 (6m 4s)
AcrySof SA60AT Alcon +ve CT Spheris* Carl Zeiss Meditec RayOne EMV +ve (+0.14 at 5.8mm) +VE Sensar AR40e Johnson & Johnson.
Scene 20 (6m 17s)
Tecnis pure see CT Asphina 509M Carl Zeiss B&L luxmart Vivity alcon (-0.55).
Scene 21 (6m 33s)
Small aperture IOL in severe cases IC-8 small aperture 1.36mm These lenses are off-label in the United States for keratoconus patients and were not FDA-approved for this specific indication. These lenses mitigate peripheral distortions through the pinhole effect, potentially improving visual acuity in eyes with irregular corneas.
Scene 22 (7m 1s)
Toric ……Multifocal. Toric ….recommended Stable (refractive and topography for 1 year) Mild to moderate KC Relatively regular central astigmatism Good visual acuity with spectacles NOT recommended (advanced ,RGP wear , progressive disease.,high difference between VA with RGP and spectacle, future keratoplasty) Multifocal ….not recommanded.
Scene 23 (7m 17s)
Intraoperative challenges. Visualization (viscoelastic agents, rigid gas permeable contact lens (Hoya Hard Ex, Hoya Corp.) Wound creation (limbal , superotemporal for inferotemporal cone and temporal for central cone ,suturing corneal incision) Capsular tension ring (CTR) prevent rotation of lens ..