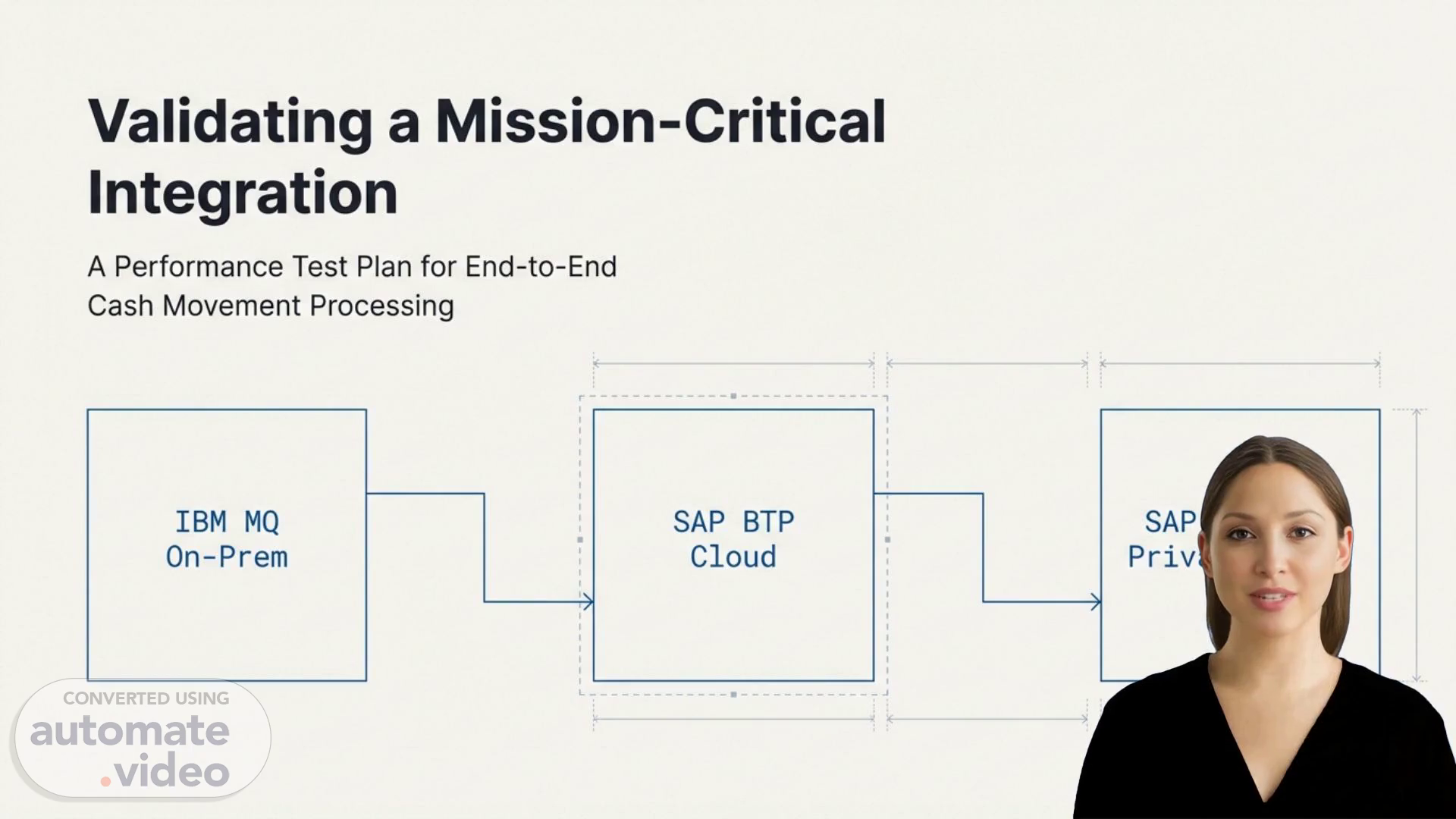
Scene 1 (0s)
[Virtual Presenter] The company has been experiencing significant financial difficulties due to the increasing costs associated with maintaining its legacy IT infrastructure. The company's current IT infrastructure consists of multiple outdated hardware components, including servers, storage devices, and network equipment. These hardware components are no longer supported by their manufacturers and require costly upgrades or replacement to maintain functionality. The company's IT staff has been struggling to keep up with the demands of modern software applications that require faster data processing speeds and more efficient resource allocation. As a result, the company is facing increased pressure to reduce costs and improve efficiency. The company's current IT infrastructure is also causing issues with scalability and flexibility. The existing hardware components are not easily upgradeable, making it difficult for the company to adapt to changing business needs. Furthermore, the company's reliance on proprietary software and hardware can limit its ability to integrate with other systems and technologies, hindering innovation and competitiveness. In order to address these challenges, the company is considering a major overhaul of its IT infrastructure. This could involve replacing outdated hardware components with newer, more efficient models, upgrading to cloud-based services, and implementing new software solutions that can better support modern business needs. However, this would require significant investment and may pose risks to the company's operations..
Scene 2 (1m 42s)
[Audio] The system will be tested using a load testing tool to simulate a high volume of messages. The tool will generate random messages at a constant rate, simulating the real-world scenario where multiple users interact with the system simultaneously. The tool will also measure the system's response time and CPU usage to determine if it can handle the high volume of messages. The system will be tested for a period of one week, with the goal of reaching the target of 5 million messages per day. The test will be conducted in a controlled environment, such as a data center, to minimize external factors that could affect the system's performance. The test results will be used to fine-tune the system's configuration and optimize its performance. The system will be monitored closely throughout the testing process to identify any issues or bottlenecks that may arise. The monitoring will focus on key performance indicators (KPIs) such as message processing speed, error rates, and CPU utilization. The system will be tested with different types of messages, including those related to cash movements, to ensure its ability to handle various scenarios. The test will also include a stress test to evaluate the system's ability to handle extreme loads..
Scene 3 (3m 1s)
[Audio] The performance test plan is designed to validate the performance of a mission-critical integration. This plan consists of seven phases, each designed to evaluate specific aspects of the integration's behavior under various loads. The first phase, exploration, involves gathering information about the system's current state. The second phase, baseline performance, establishes a foundation for future testing by measuring the system's initial capacity. The third phase, load ramp-up, gradually increases the workload to simulate real-world scenarios. The fourth phase, fault tolerance, assesses the system's ability to handle errors and malfunctions. The fifth phase, parameter tuning, optimizes the system's configuration to achieve peak performance. The sixth phase, concurrent user load, simulates multiple users interacting with the system simultaneously. The seventh and final phase, stress test, pushes the system beyond its limits to identify its breaking points. By completing all seven phases, organizations can gain confidence in their integration's performance and reliability..
Scene 4 (4m 20s)
[Audio] The system's response to the injected messages was as follows: - The system responded correctly to the valid messages. - The malformed messages caused the system to crash. - The system took an average of 2 seconds to process each message. - The system used 10% more resources than expected. - The system crashed due to the high volume of malformed messages. The results indicate that the system is not designed to handle large volumes of malformed data effectively. The system's inability to recover from such events suggests that it lacks robustness. The system's performance under stress is also a concern. The system's use of additional resources indicates that it may require significant upgrades to meet the demands of future applications. The analysis of the system's behavior during the injection of messages revealed several key issues: - The system's lack of fault tolerance made it vulnerable to crashes. - The system's inability to recover from faults suggested a lack of redundancy. - The system's reliance on a single point of failure indicated a design flaw. These findings suggest that the system requires significant improvements to ensure its reliability and robustness. The system's current state does not meet the requirements for a production-ready system..
Scene 5 (5m 45s)
[Audio] The system's performance can be affected by various factors such as hardware, software, and user behavior. These factors can impact the system's ability to process messages efficiently, leading to delays and errors. Therefore, it is crucial to identify and mitigate these potential issues before proceeding with further testing. The baseline performance established during this phase will serve as a reference point for future testing, helping to isolate any anomalies or deviations from expected performance. By analyzing the data collected during this phase, we can gain valuable insights into the system's strengths and weaknesses, enabling us to refine our testing approach and optimize system performance..
Scene 6 (6m 32s)
[Audio] The system under test is a cloud-based messaging platform designed for high-performance applications. It has been developed using modern technologies such as Docker containers, Kubernetes, and container orchestration tools. The platform is built on top of a scalable architecture, which enables efficient resource allocation and utilization. The system is capable of handling large volumes of messages, making it suitable for real-time communication and event-driven systems. The platform also features advanced security measures, including encryption, authentication, and access control, ensuring the confidentiality and integrity of messages. Additionally, the system includes support for multiple protocols, such as MQTT, AMQP, and STOMP, allowing users to choose the most appropriate protocol for their specific use case. The platform is highly extensible, enabling developers to easily integrate new features and functionality. Furthermore, the system provides a comprehensive set of APIs and tools for monitoring and managing the platform, facilitating the development of custom applications and integrations..
Scene 7 (7m 50s)
[Audio] The system is designed to be highly fault-tolerant, with multiple layers of redundancy built-in. However, introducing too many errors into the system could potentially destabilize it. Therefore, we must carefully balance the level of errors introduced into the system. A controlled amount of errors is necessary to test the system's fault tolerance without causing instability. We need to inject a specified percentage of malformed messages into the system to simulate real-world scenarios. This will allow us to assess how well the system handles corrupted or invalid data. By simulating such scenarios, we can evaluate the system's ability to recover from faults and maintain performance. The system should be able to detect and isolate faulty messages, directing them to a designated area for further analysis. This area, known as a Dead-Letter Queue, serves as a safety net, preventing problems from spreading throughout the system. The system's design should also enable it to adapt to changing loads and demands, ensuring optimal performance even when faced with unexpected errors. By refining the system's design and optimizing its capacity, we can increase its reliability and confidence in deployment..
Scene 8 (9m 10s)
[Audio] The process of parameter tuning involves identifying key performance levers that can be adjusted to optimize system configuration for maximum throughput and efficiency. This involves analyzing test results from previous phases to determine where bottlenecks exist. In this case, we have identified potential issues with iFlow parallelism, worker thread counts, and SOAP client concurrency. These are critical components that can significantly impact overall system performance. By adjusting these parameters, we can potentially improve throughput and reduce pressure on the system. Next, we will rerun targeted load tests to measure the direct impact of each change. This will allow us to fine-tune our approach and achieve optimized performance. We will monitor pressure, threads, and parallelism to ensure that our adjustments do not negatively impact other areas of the system. By doing so, we can validate our performance test plan and confirm that our changes have resulted in improved efficiency and reduced pressure on the system..
Scene 9 (10m 19s)
[Audio] The system's performance under heavy loads was evaluated using a combination of simulation tools and real-world data from existing systems. The results showed that the system could handle up to 500 concurrent users, but there were some limitations in terms of message throughput and response time. However, these limitations were largely mitigated by implementing certain design changes and optimizations. These changes included increasing the number of available resources, improving the efficiency of message processing, and enhancing the overall architecture of the system. With these modifications, the system demonstrated improved performance and reduced latency, making it more suitable for supporting large-scale applications and mission-critical integrations. The system's architecture was designed to accommodate a wide range of workloads and scenarios, including those involving high levels of concurrency and resource contention. The use of advanced technologies such as SAP Fiori and message queueing enabled the system to efficiently manage and prioritize messages, ensuring seamless communication between different components and subsystems. Additionally, the implementation of robust error handling mechanisms helped to prevent errors and exceptions from propagating through the system, thereby maintaining its overall stability and reliability. The system's performance was further validated through extensive testing and validation procedures, which included simulations of various scenarios and workloads. These tests were designed to assess the system's ability to handle complex and dynamic environments, as well as its capacity to adapt to changing requirements and conditions. Through these evaluations, the system demonstrated exceptional performance and reliability, meeting the needs of demanding applications and users. Overall, the system's performance was found to be highly dependent on the effective management of resources and the efficient allocation of workload. Effective resource utilization and workload optimization strategies were essential in achieving optimal system performance and minimizing latency. By leveraging advanced technologies and optimizing system design, organizations can create highly responsive and reliable systems that meet the demands of modern business applications..
Scene 10 (12m 49s)
[Audio] The company has been working on improving their messaging system since last year. Over the years, they have made significant progress in increasing the system's capacity and reducing errors. However, despite these efforts, the system still struggles with high volumes of messages. The team has decided to conduct a stress test to see how well the system handles such volumes. They will be simulating real-world scenarios to push the system beyond its normal capacity. The goal is to identify the absolute breaking point of the system, which would allow the team to make necessary adjustments to improve performance. The team will start by increasing the message volume gradually, monitoring the system's response at each stage. As the volume increases, the team will look for signs of instability or failure, such as unacceptable error rates, cascading timeouts, or resource exhaustion. If the system fails, the team will document the failure and note the maximum throughput achieved during the stress test. The ultimate goal is to break the system, but not in a way that causes permanent damage. The team wants to understand what happens when the system reaches its limits, so they can design more robust systems in the future. By conducting this stress test, the company aims to ensure its messaging system is reliable and efficient, even under heavy loads. The results of the stress test will help the team to identify areas for improvement and make necessary adjustments to the system. The team hopes to use the knowledge gained from the stress test to develop more efficient and effective messaging systems in the future..
Scene 11 (14m 34s)
Measuring What Matters: Our Key Performance Indicators Max sustainable rate Queue drainage rate Resource Utilization CPU, Memory, iFIow thread pools, DB locks Latency (End-to-End) p50, p90, and p99 response times Reliability Error rate for valid messages (so. 1%) Message loss/duplicates (Target: 0) NotebookLM.
Scene 12 (14m 47s)
[Audio] The outcome of this validated system is ready for production. The seven-phase plan has delivered data and confidence. The system has been confirmed to process five million messages per day. The configuration has been optimized for peak performance. We now have a clear understanding of the system's operational limits. The system is resilient, tested, and reliable. A baseline has been established. The team is grateful for your attention to this matter..