New GCSE cells notes
Scene 1 (0s)
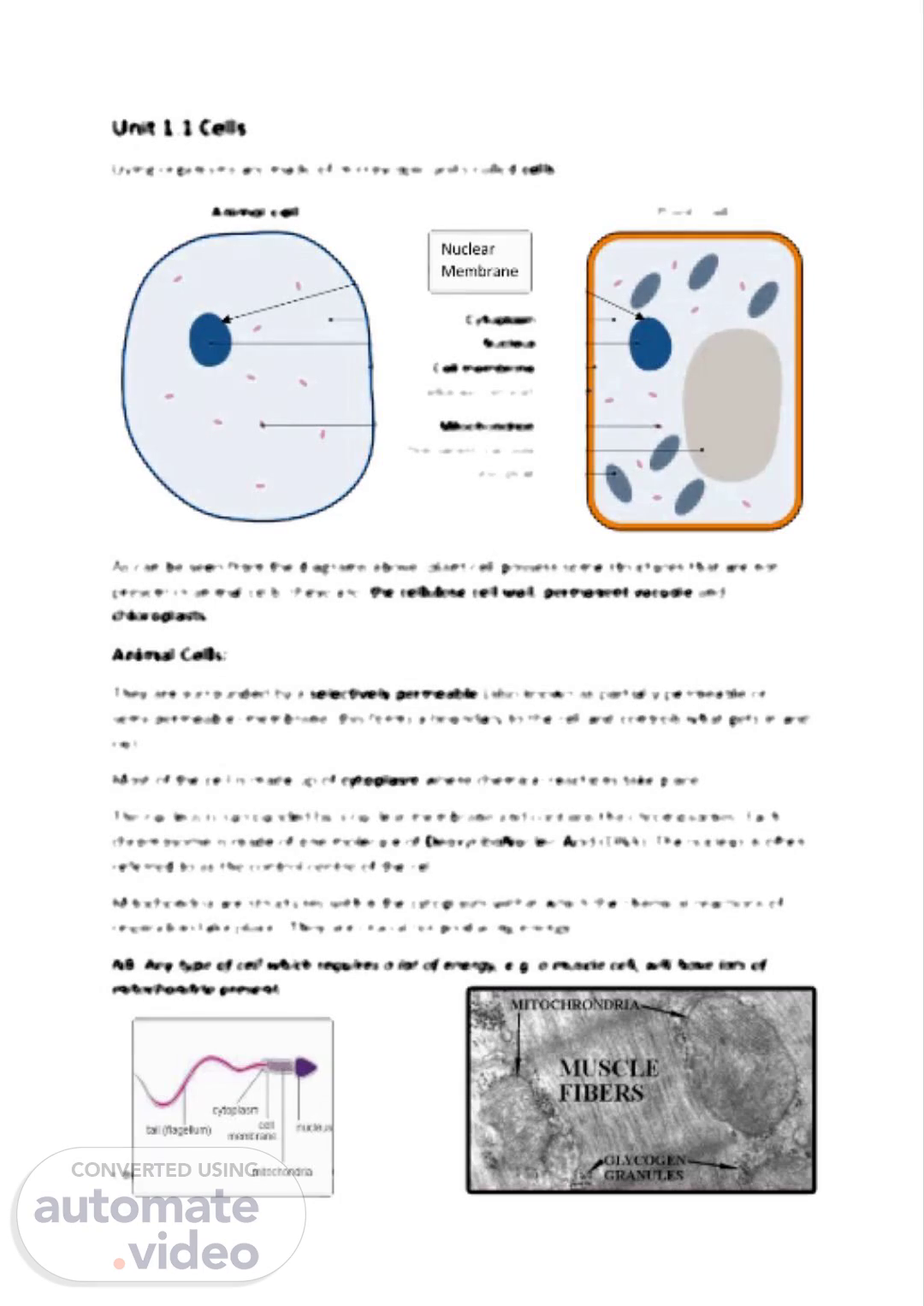
Unit 1.1 Cells Living organisms are made of microscopic units called cells. As can be seen from the diagrams above, plant cell possess some structures that are not present in animal cells, these are: the cellulose cell wall, permanent vacuole and chloroplasts. Animal Cells: They are surrounded by a selectively permeable (also known as partially permeable or semi-permeable) membrane, this forms a boundary to the cell and controls what gets in and out. Most of the cell is made up of cytoplasm where chemical reactions take place. The nucleus is surrounded by a nuclear membrane and contains the chromosomes. Each chromosome is made of one molecule of DeoxyriboNucleic Acid (DNA). The nucleus is often referred to as the control centre of the cell. Mitochondria are structures within the cytoplasm within which the chemical reactions of respiration take place. They are crucial for producing energy. NB: Any type of cell which requires a lot of energy, e.g. a muscle cell, will have lots of mitochondria present. Complete the following table: Nuclear Membrane.
Scene 2 (1m 3s)
[Audio] Cells are fundamental to living organisms with functions such as providing structure and performing vital processes. Plant and animal cells contain similar components such as the cell membrane cytoplasm nuclear membrane and nucleus and mitochondria. However plants additionally have a cell wall made of cellulose a large vacuole and chloroplasts with chlorophyll. The cell wall and vacuole strengthen the cell while the chloroplasts and chlorophyll are used for photosynthesis. Bacteria do not possess a cellulose cell wall but they do have a thin flexible layer called the cell wall to provide structure and protection. Complete the table on the components specific to plant cells and their functions then move on to the next slide..
Scene 3 (1m 53s)
[Audio] All cells whether they are plant animal or bacterial have some features in common. They each contain cytoplasm a cell membrane and DNA. Additionally they can be observed by using a microscope which magnifies the image and allows us to differentiate between the cells. The most notable differences between the three cells are the elements that they contain. Plant cells have a cell wall made of cellulose a permanent vacuole and chloroplasts. Animal cells are enclosed by a selectively permeable membrane and contain nuclei cytoplasm and mitochondria. The smallest and simplest of the three cells are bacterial cells which lack a true nucleus. D-N-A in bacterial cells is found in a single circular strand located in the cytoplasm and some contain plasmids. These bacterial cells have a cell wall however it is not composed of cellulose..
Scene 4 (2m 47s)
[Audio] Cells are truly incredible. The largest among human cells such as the skin cell are 20 times smaller than a single grain of salt. Magnifying lenses like microscopes are necessary to see these otherwise invisible structures. To observe cells under a microscope a slide must be created. To make a slide for plant cells one needs to take a thin slice of onion and add a drop of water or iodine. Animal cells can be observed by taking a cotton swab to the inside of the cheek and smearing it on a slide; adding a drop of methylene blue can further enhance the ability to view the cell structure in more detail..
Scene 5 (3m 43s)
[Audio] Cells are the most basic units of all living things. With the help of a microscope we can observe the distinctions between plant and animal cells. When using a light microscope it is best to start with the low power objective lens as it provides a wider field of view making it possible to spot more cells. After you have identified the cell you are looking for use a higher power lens for a more precise view but be extra cautious when zooming in as the slide is close to the lens. The eyepiece lens typically has a magnification of 10x so with an objective lens of 40x the total magnification is 400x. The total magnification for an objective lens of 20x or 100x would be 200x or 1000x respectively. Sketching out cell structures is an effective method for better understanding the structure of cells and the differences between plant and animal cells..
Scene 6 (4m 44s)
[Audio] Cells are so small that they can only be observed under a microscope. To make them visible a drawing or photograph must be created. To ensure accuracy the image must be properly labeled and must be on scale with the observed cell. To calculate the magnification length of image and actual size of the cell the equation Magnification = Length of Image/Actual Length must be used. It is important to note that all measurements must be in the same unit (metres (m) millimetres (mm) or micrometres (µm)). To convert 1 meters is equal to 1000 millimeters and 1 meters is equal to 1000000 µm. The equation can also be rearranged to calculate the actual length of the cell and/or to determine the magnification used. When creating a biological drawing remember to draw in pencil use the same proportions as the observed cell label using separate ruled lines give the drawing a title including magnification or size and use the equation above to make accurate calculations..
Scene 7 (5m 56s)
[Audio] Cells are incredibly small so small that our eyes cannot observe them. Special tools like electron microscopes allow us to explore more about them. An electron microscope can magnify up to 100000 times of the original cell size. A scale bar is used in order to calculate the magnification. This is done by dividing the scale bar image length by the actual length of the scale bar. An onion cell can be observed more closely with the help of this microscope. Its length can be calculated by the same process. This way electron microscopes can help us learn more about cells..
Scene 8 (6m 34s)
[Audio] Cells are incredibly small units that form the building blocks of all living organisms. They are comprised of a nucleus cytoplasm and a selectively permeable cell membrane. To observe the details of cells we require a magnification of around x1500. The resolution of the microscope however restricts what we can see. To look inside the tiny structures of a cell such as the chloroplast and mitochondrion a more powerful microscope such as an electron microscope is needed due to its greater resolution allowing us to discern details 0.0001µm apart showcasing the complexity of a cell. Moreover a process called diffusion is necessary for the free movement of substances such as oxygen water dissolved food molecules mineral ions carbon dioxide and nitrogen wastes in and out of the cell. This movement is essential for the cell's functioning allowing it to survive and prosper..
Scene 9 (7m 36s)
[Audio] Cells are the fundamental building blocks of all living organisms. They can be divided into two main categories plant and animal cells. Both types of cells have a cell membrane that helps them to function and is selectively permeable meaning it allows some substances to pass through but not all. The rate of diffusion of substances within the cell is determined by the concentration gradient temperature and surface area. As the concentration gradient or surface area increases or temperature rises diffusion rate increases. Diffusion is important for the movement of oxygen and carbon dioxide between the air and living organisms such as in the lungs or in leaves. The size of the surface area and volume have an impact on the rate of diffusion with a larger surface area providing for a faster rate..
Scene 10 (8m 28s)
[Audio] Cells are the smallest components that make up all living organisms. They are divided into two categories: plant cells and animal cells. Plant cells have a cellulose cell wall a permanent vacuole and chloroplasts while animal cells are enclosed by a selectively permeable membrane and consists of a nucleus cytoplasm and mitochondria. The size of a cell is important as it relates to the amount of oxygen and other substances needed for its reactions. The larger the cell the more oxygen required but too big of a cell will not have enough surface area to allow the necessary oxygen to enter. This is why single celled organisms are small and multicellular ones rely on gas exchange organs like lungs and a system like the circulatory system to deliver oxygen. This knowledge helps us to better understand life and physiology..
Scene 11 (9m 29s)
[Audio] Cells are the building blocks of life. They form all living organisms and can be classified as plant cells and animal cells. Plant cells have cell walls permanent vacuoles and chloroplasts whereas animal cells are surrounded by a selectively permeable membrane and feature a nucleus cytoplasm and mitochondria. Single-celled organisms perform all their necessary life processes within the one cell. However in multicellular organisms cells differentiate and become specialized. These distinct cells are not randomly dispersed in the organism but instead are organized into groups known as tissues organs and organ systems. These various tissues organs and organ systems all have specific functions and main organs such as the heart and veins in the circulatory system which transports essential substances around the body. Understanding cells and how they are organized into tissue organs and organ systems is essential for comprehending how living organisms work..
Scene 12 (10m 31s)
[Audio] Cells are the fundamental building blocks of all living organisms. In this presentation we will discuss stem cells a special type of cell capable of replicating itself or differentiating into other cell types. Stem cells can be obtained from embryos umbilical cords or adult bone marrow. Embryonic stem cells can give rise to a broad range of cell types while adult stem cells from bone marrow are generally more restricted to blood cells. In recent years stem cell research has gained attention as it holds the promise of curing certain ailments and restoring damaged tissues. It is essential to be aware of the ethical considerations around stem cell research while being mindful of its potential benefits..
Scene 13 (11m 19s)
[Audio] Cells are an integral part of all living organisms and they can vary in type and structure. Plant cells and animal cells have different characteristics and we explored these differences. We also looked at the potential use of stem cells in medicine and the benefits and risks associated with them. Treatments of leukaemia and other conditions are made possible through stem cell transplants although there can be serious risks of infection and tumours or diseases crossed over from other animals. Ethical issues arise when embryonic stem cells are involved and governments must regulate research accordingly. Peer review in science is important as it ensures that conclusions drawn from investigations are accurate. As we come to the end of our presentation I would like to thank you for your attention..