Introduction-to-Stem-Cells
Scene 1 (0s)
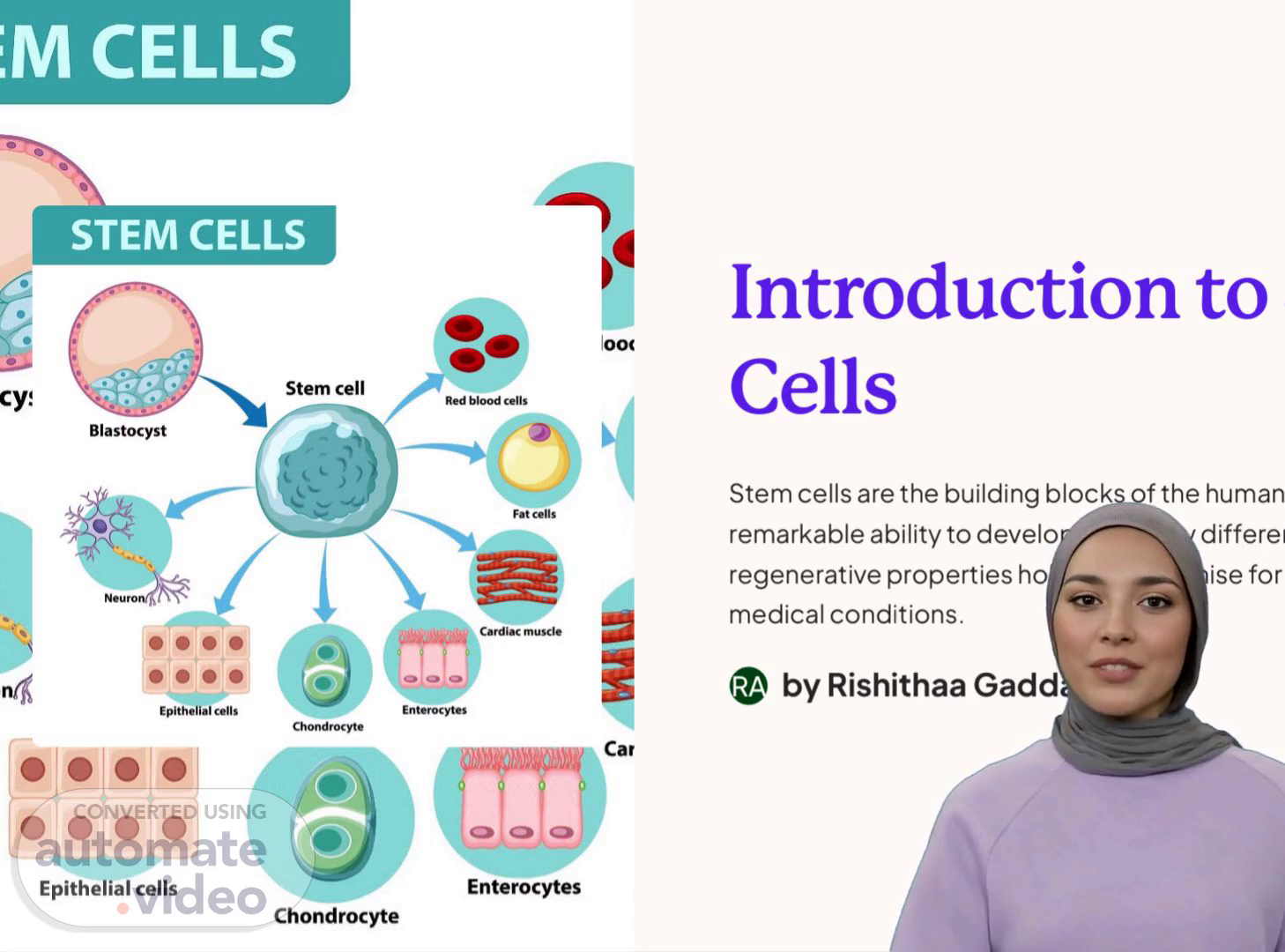
[Virtual Presenter] Introduction to Stem Cells Stem cells are the building blocks of the human body with the remarkable ability to develop into many different cell types. Their regenerative properties hold great promise for treating a wide range of medical conditions. RA by Rishithaa Gaddam.
Scene 2 (20s)
[Virtual Presenter] Types of Stem Cells Embryonic Stem Cells Derived from embryos with the potential to develop into any type of cell. Adult Stem Cells Found in specific tissues capable of differentiating into multiple cell types within their own tissue. Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells (iPSCs) Adult cells reprogrammed to exhibit embryonic stem cell-like properties by introducing specific genes..
Scene 3 (49s)
[Audio] Properties of stem cells Self-renewal: Stem cells can divide and create copies of themselves indefinitely. Pluripotency: They have the potential to differentiate into various cell types. Quiescence: They can remain inactive for long periods until activated by injury or disease..
Scene 4 (1m 9s)
[Audio] Stem Cell Differentiation 1 Embryonic Differentiation During embryonic development stem cells differentiate into specialized cell types like neurons muscles and skin cells. 2 Adult Stem Cell Differentiation Adult stem cells differentiate to replenish and repair specific tissues such as bone marrow cells producing blood cells. 3 Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells Using specific factors adult cells can be reprogrammed into pluripotent stem cells capable of differentiating into various cell types..
Scene 5 (1m 48s)
[Audio] Stem Cell Niches Stem cell niches also known as microenvironments play a crucial role in regulating stem cell behavior and maintaining their unique properties. These specialized areas provide the necessary signals and support for stem cell maintenance self-renewal and differentiation. Understanding the complex interactions within these niches is essential for harnessing the full potential of stem cells in regenerative medicine..
Scene 6 (2m 18s)
[Audio] Applications of Stem Cells in Research Stem cells have diverse applications in scientific research. They are used to study development model diseases and screen potential drug candidates. Researchers also use stem cells to investigate cellular processes tissue regeneration and transplantation techniques..
Scene 7 (2m 38s)
[Audio] Therapeutic Potential of Stem Cells Tissue Regeneration Stem cells have the potential to repair and regenerate damaged tissues and organs in the body. Drug Testing & Development Stem cells can be utilized to test new drugs and develop personalized treatments for various diseases. Immune System Modulation They can be used to modulate immune responses and combat autoimmune diseases. Neurological Disorders Potential for treating neurological disorders like Parkinson's and Alzheimer's disease..
Scene 8 (3m 12s)
[Audio] Challenges in Stem Cell Therapy Immune Rejection 1 Host immune system attacking transplanted cells 2 Tumor Formation Risk of abnormal growth from stem cell therapy Effectiveness 3 Varying success rates across different treatment types Regulatory Challenges 4 Legal and ethical considerations in treatment development.
Scene 9 (3m 38s)
[Audio] Ethical Considerations in Stem Cell Research Equitable Access Human Dignity Informed Consent Regulatory Oversight Respecting the Addressing issues of inherent value of accessibility and Ensuring that Establishing human life when affordability of stem individuals fully stringent guidelines understand the to govern the working with cell therapies for all potential risks and responsible conduct embryonic stem socioeconomic benefits of of stem cell research cells. groups. participating in stem ensuring safety and Striking a delicate Aiming for fair cell research. ethical integrity. balance between distribution of scientific progress benefits and Protecting the Creating a autonomy and rights framework for ethical and ethical burdens. of research decision-making responsibility. participants. and accountability..
Scene 10 (4m 39s)
[Audio] Practical Challenges Laboratory Research Culture and Handling Regulatory Compliance Interdisciplinary Collaboration Conducting stem cell Maintaining stem cell Adhering to strict Working across research in state-ofcultures under regulatory guidelines diverse scientific the-art laboratories controlled sterile and ethical disciplines fostering with advanced conditions with considerations in all effective equipment. meticulous attention stages of stem cell communication and to detail. research. collaboration for comprehensive research..
Scene 11 (5m 15s)
[Audio] Tumorigenicity and Safety Concerns Stem cell research raises concerns about the potential for tumor formation a phenomenon known as tumorigenicity. Managing safety concerns related to stem cell therapy is crucial for clinical applications..
Scene 12 (5m 33s)
[Audio] Immune Rejection Hostile Immune Response Need for Immunomodulation Immunosuppressive Medications Organ or tissue rejection Strategies are essential to Usage of drugs that by the recipient's immune dampen the immune suppress the immune system involves attacking response and prevent system to prevent the transplanted cells or rejection of stem cell rejection but they pose tissue. transplants in medical risks and complications. treatments..
Scene 13 (6m 5s)
[Audio] Commercialization and Regulation Unregulated treatments: Highlight the risks of unproven and unregulated stem cell therapies. Advocacy for regulation: Emphasize the need for robust regulatory frameworks to ensure safety and evidence-based practices. Ethical considerations: Discuss the ethical implications of commercializing stem cell treatments without proper regulation..
Scene 14 (6m 34s)
[Audio] Responsible Development and Delivery Scientific Rigor Patient Safety Emphasizing scientific validity and Ensuring the well-being and safety of accuracy in research and development. patients in stem cell therapies. Regulatory Oversight Establishing and adhering to robust regulatory frameworks..
Scene 15 (6m 56s)
[Audio] Future Directions in Stem Cell Biology Potential Challenges Stem cell research offers vast potential for Technical ethical and practical challenges regenerative medicine disease modeling and must be addressed to realize the full potential drug development. of stem cell therapies. The ability to repair and replace damaged Regulatory oversight is essential to ensure the tissues holds promise for addressing numerous safe and responsible development of stem cell medical conditions. technologies. International… AI Integration International Collaboration AI Integration Regenerative… Genetic… Regenerative Medicine Genetic Engineering The future of stem cell biology involves increased international collaboration to share knowledge and drive progress. Integrating artificial intelligence (A-I---) in research and treatment development is also a key direction. Furthermore regenerative medicine and genetic engineering will continue to play vital roles in advancing stem cell applications..