Page 1 (0s)
WELCOME.
Page 2 (39s)
COVERAGE TOPIC. 01. SOLAR SYSTEM. 02. HELIOCENTRIC AND GEOCENTRIC.
Page 3 (1m 57s)
To know and understand the concept of Solar system.
Page 4 (2m 59s)
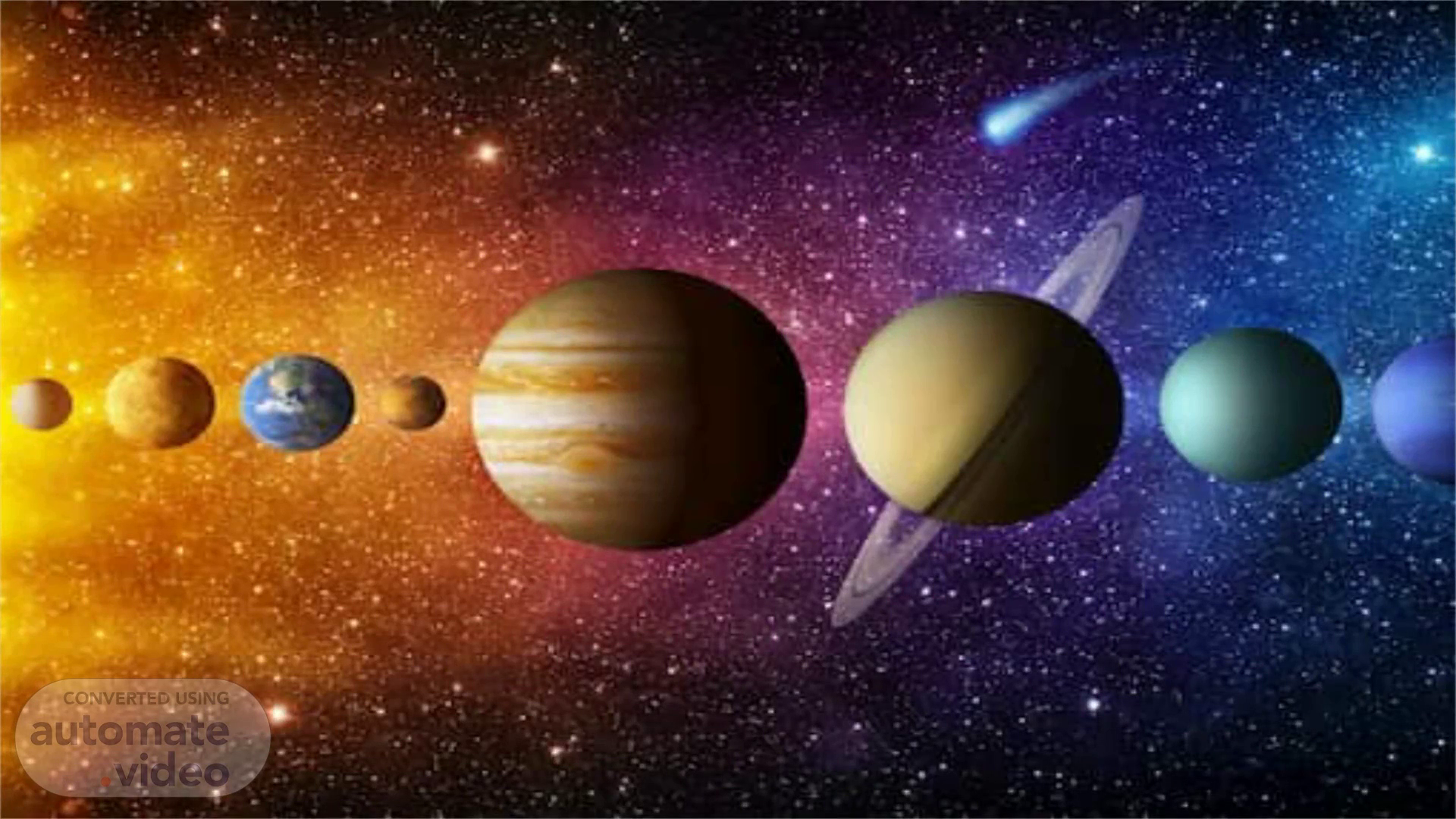
SOLAR SYSTEM. PRESENTED BY: LEA CLORDO JOVEN.
Page 5 (3m 17s)
. MILKY WAY GALAXY. SOLAR SYSTEM. abstract.
Page 6 (4m 11s)
SOLAR SYSTEM. Solar System is a Planetary System.
Page 7 (6m 12s)
THE SUN. Our Sun is the star at the center of our Solar System..
Page 8 (8m 11s)
ILLUSTRATION OF SOLAR SYSTEM. abstract. 2 CATEGORIES.
Page 9 (9m 55s)
MERCURY. VENUS. EARTH. MARS. TERRESTRIAL PLANETS.
Page 10 (10m 15s)
IMAGE OF MERCURY. THE MERCURY. Mercury is the smallest planet in the Solar System and the closest to the Sun..
Page 11 (11m 59s)
THE VENUS. It is the Second among the Terrestrial planets in the Solar System..
Page 12 (14m 46s)
IMAGE OF MERCURY. THE EARTH. Earth is the third terrestrial planet in the Solar System which is the only planet that can support and sustain life.
Page 13 (16m 41s)
THE MARS. It is the fourth planet that revolves around the Sun..
Page 14 (19m 14s)
ASTEROID BELT. .
Page 15 (19m 39s)
ASTEROID BELT. The Asteroid Belt (sometimes referred to as the main asteroid belt) orbits between Mars and Jupiter. It consists of asteroids and minor planets forming a disk around the sun..
Page 16 (21m 24s)
CERES. Largest object. (About the same size as Texas).
Page 17 (21m 47s)
JUPITER. SATURN. URANUS. NEPTUNE. JOVIAN PLANETS.
Page 18 (22m 39s)
THE JUPITER. It is the fifth planet that orbits around the Sun. Known as the “Largest Planet” in the Solar System..
Page 19 (24m 28s)
IMAGE OF SATURN. THE SATURN. It is the sixth planet in the Solar system that revolves around the Sun and the second largest planet in the Solar System..
Page 20 (26m 53s)
THE URANUS. It is the seventh planet from the Sun, and has the third-largest diameter in our solar system. It was the first planet found with the aid of a telescope.
Page 21 (28m 54s)
IMAGE OF NEPTUNE. THE NEPTUNE. It is the eight and most distant planet in our solar system..
Page 22 (31m 28s)
O*ctsarenottoscale Sun Logariåncscale Solar system distances Inner Oort Cloud Main asteroidbelt Kui*rBelt 10 Astonomlcalunits (AU) OortCloud 10,000 10000.
Page 23 (31m 39s)
KUIPER BELT. Kuiper Belt KTI!bSL. I s a circumstellar disc in the outer Solar System, extending from the orbit of Neptune at 30 astronomical units to approximately 50 AU from the Sun..
Page 24 (32m 23s)
OORT CLOUD. . Collection of Icy debris. The edge of the Solar System.
Page 25 (32m 47s)
Last Image on solar system..
Page 26 (33m 16s)
HELIOCENTRIC AND GEOCENTRIC.
Page 27 (33m 48s)
Moving sky.
Page 28 (34m 6s)
APPARENT DAILY MOTION.
Page 29 (34m 48s)
PLATO. ARISTOTLE. PTOLEMY. GEOCENTRIC MODEL OF THE UNIVERSE.
Page 30 (35m 33s)
GEOCENTRIC THEORY. Geocentric makea. A theory model of the Solar System in which the stationary earth lies at the center and all other celestial objects orbit it..
Page 31 (36m 15s)
Video of geocentric model.
Page 32 (37m 37s)
COPERNICUS. GALILEO. HELIOCENTRIC MODEL OF THE UNIVERSE.
Page 33 (38m 36s)
HELIOCENTRIC THEORY. abstract. A model of the universe in which the SUN lies in the center and other celestial objects including earth orbit it. The earth both rotates and revolves..
Page 35 (40m 20s)
KEPLER. NEWTON. . abstract.
Page 36 (43m 5s)
THE REASON THAT KEEPS THE PLANETS ON THEIR ORBITS.
Page 38 (43m 57s)
2 FACTORS KEEPING THE PLANETS ON THEIR ORBITS. 1. GRAVITY.
Page 39 (46m 43s)
THANK YOU FOR LISTENING!. - Teacher Lhey.