Scene 1 (0s)
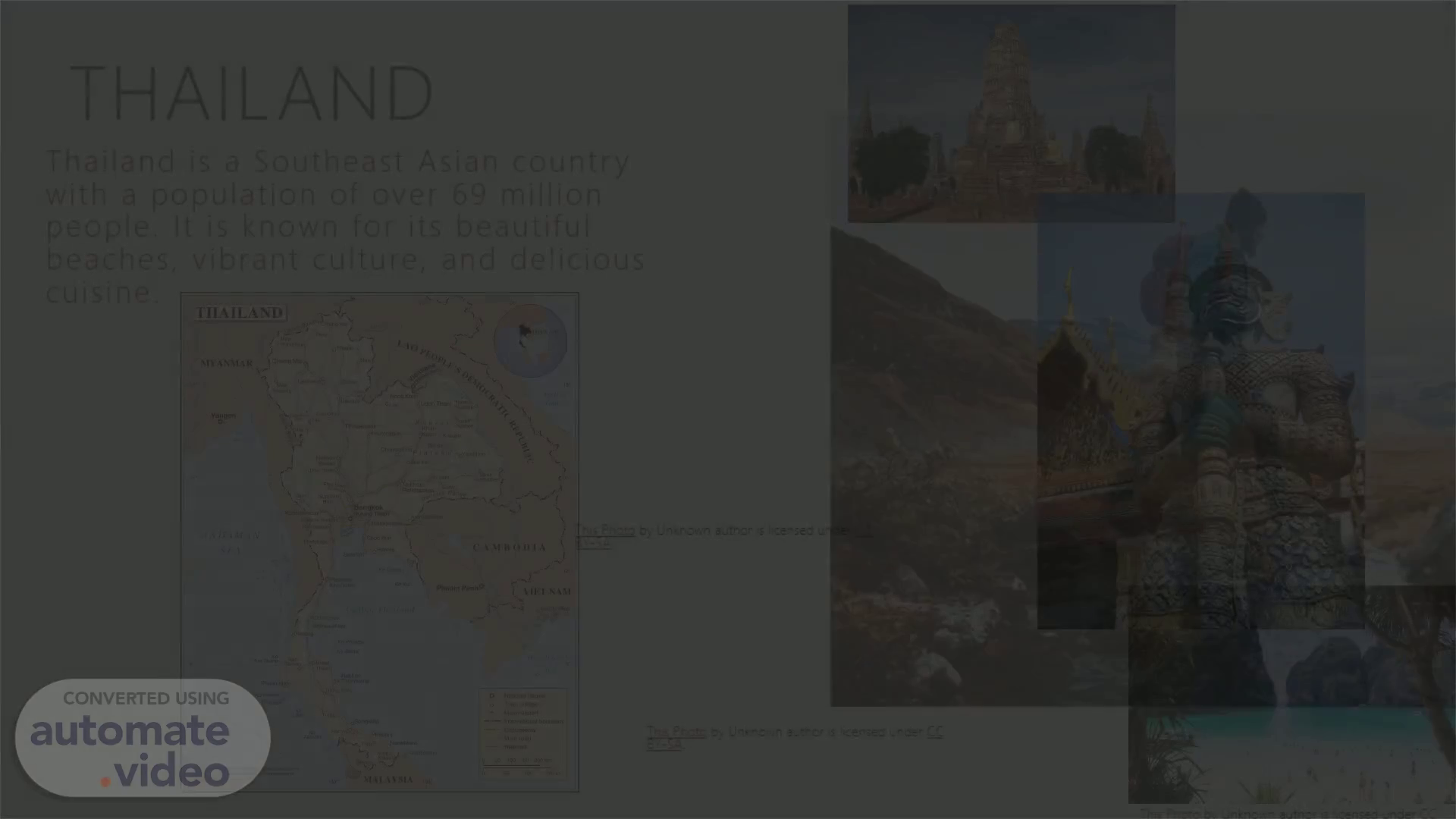
[Audio] Hello everyone and welcome to my presentation. Let's go ahead and have a look to Thailand. Thailand Thailand is a Southeast Asian country with a population of over 69 million people. It is known for its beautiful beaches, vibrant culture, and delicious cuisine..
Scene 2 (29s)
[Audio] Thailand has a rich history and culture, with influences from neighboring countries and the West. It was previously known as Siam and was ruled by various monarchs for centuries until it became a constitutional monarchy in 1932. Today, Thailand is a popular tourist destination, with millions of visitors coming to explore its stunning natural landscapes, bustling cities, and unique cultural experiences..
Scene 3 (56s)
[Audio] Thailand is also a major exporter of rice, rubber, and other agricultural products, and its economy has been growing rapidly in recent years. However, the country still faces challenges related to income inequality, political instability, and human rights issues. Let's go to Foreign Policy..
Scene 4 (1m 26s)
[Audio] Foreign Policy: It is based on the principle of "active engagement," which aims to promote regional stability, economic growth, and cooperation in Southeast Asia and beyond. The country maintains strong diplomatic relations with its neighbors, including China, Japan, and the ASEAN countries, and has also developed partnerships with countries in other regions, such as the United States, Europe, and the Middle East..
Scene 5 (1m 54s)
[Audio] Thailand is a founding member of ASEAN and plays an active role in the organization, advocating for greater regional integration and cooperation. The country has also been involved in peacekeeping operations and humanitarian assistance efforts in conflict-affected areas, such as in neighboring Myanmar..
Scene 6 (2m 14s)
[Audio] Thailand's foreign policy priorities also include promoting economic growth and trade, with a focus on expanding its markets in the region and beyond. The country has been actively pursuing free trade agreements with a number of countries, including the United States, China, and Japan..
Scene 7 (2m 33s)
[Audio] In recent years, Thailand's foreign policy has faced challenges due to political instability and changes in leadership. Nevertheless, the country remains an important player in the region and a key partner for many countries around the world. Now, let's go to economic policy..
Scene 8 (2m 53s)
[Audio] Thailand's economic policy is aimed at achieving sustainable and inclusive economic growth and development, with a focus on promoting innovation, enhancing competitiveness, and reducing inequality..
Scene 9 (3m 9s)
[Audio] The government's economic policies are implemented through the National Economic and Social Development Plan (NESDP), a five-year plan that outlines the country's development priorities and strategies. The current NESDP, covering 2017-2021, emphasizes the development of the Eastern Economic Corridor (EEC) as a hub for high-tech industries, infrastructure development, and investment promotion..
Scene 10 (3m 37s)
[Audio] Thailand's economy is largely export-oriented, with exports accounting for a significant share of GDP. The country's main exports include electronics, automobiles, and agricultural products such as rice and rubber. The government has been promoting the development of new industries, such as renewable energy and digital technology, to diversify the country's export base and enhance its competitiveness..
Scene 11 (4m 5s)
[Audio] To attract foreign investment, the government has implemented a number of policies to improve the business environment, including measures to streamline regulations and reduce bureaucracy. The country has also been promoting regional economic integration through its participation in free trade agreements, including the ASEAN Free Trade Area and the recently established Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership (RCEP)..
Scene 12 (4m 31s)
[Audio] Despite these efforts, Thailand still faces challenges related to income inequality, labor productivity, and the need to upgrade its infrastructure. The government has launched a number of initiatives to address these issues, including programs to provide skills training to workers and to improve the quality of education. Next, we have advantage and disadvantage of the economic policy..
Scene 13 (4m 56s)
[Audio] Diversification of the economy through the development of new industries such as renewable energy and digital technology Attraction of foreign investment through improved business environment and participation in free trade agreements Strong export-oriented economy with a significant share of GDP coming from exports.
Scene 14 (5m 19s)
[Audio] Promoting innovation and enhancing competitiveness to achieve sustainable economic growth and development Development of the Eastern Economic Corridor (EEC) as a hub for high-tech industries, infrastructure development, and investment promotion Investment in education and skills training programs to address issues related to income inequality and labor productivity..
Scene 15 (5m 44s)
[Audio] Dependence on a few key industries, such as electronics, automobiles, and agricultural products, which makes the economy vulnerable to external shocks Uneven distribution of economic benefits, with income inequality remaining a challenge Need to upgrade infrastructure, particularly in rural areas, to support sustainable economic growth Environmental degradation caused by industrial development, particularly in the EEC Difficulty in balancing the needs of economic growth with social and environmental concerns Now, let's go to advantages and disadvantages of Thailand's foreign policy..
Scene 16 (6m 28s)
[Audio] Active engagement in the region and beyond to promote regional stability, economic growth, and cooperation Strong diplomatic relations with neighboring countries and partnerships with countries in other regions, such as the United States, Europe, and the Middle East Founding member and active participant in ASEAN, advocating for greater regional integration and cooperation..
Scene 17 (6m 53s)
[Audio] Involvement in peacekeeping operations and humanitarian assistance efforts in conflict-affected areas, such as in neighboring Myanmar Promotion of economic growth and trade through free trade agreements and investment promotion policies..
Scene 18 (7m 9s)
[Audio] Challenges related to political instability and changes in leadership, which can affect the continuity of the country's foreign policy. Tension with neighboring countries over territorial disputes and other issues, such as the ongoing conflict in Myanmar Need to balance its relationships with major powers such as the United States and China, which can have different interests in the region Criticism from human rights groups over the country's handling of human rights issues, particularly with regards to the treatment of refugees and asylum seekers. Thank you for listening. This ends my presentation..