In a relational data model, which one of the following statements is TRUE?
Scene 1 (0s)
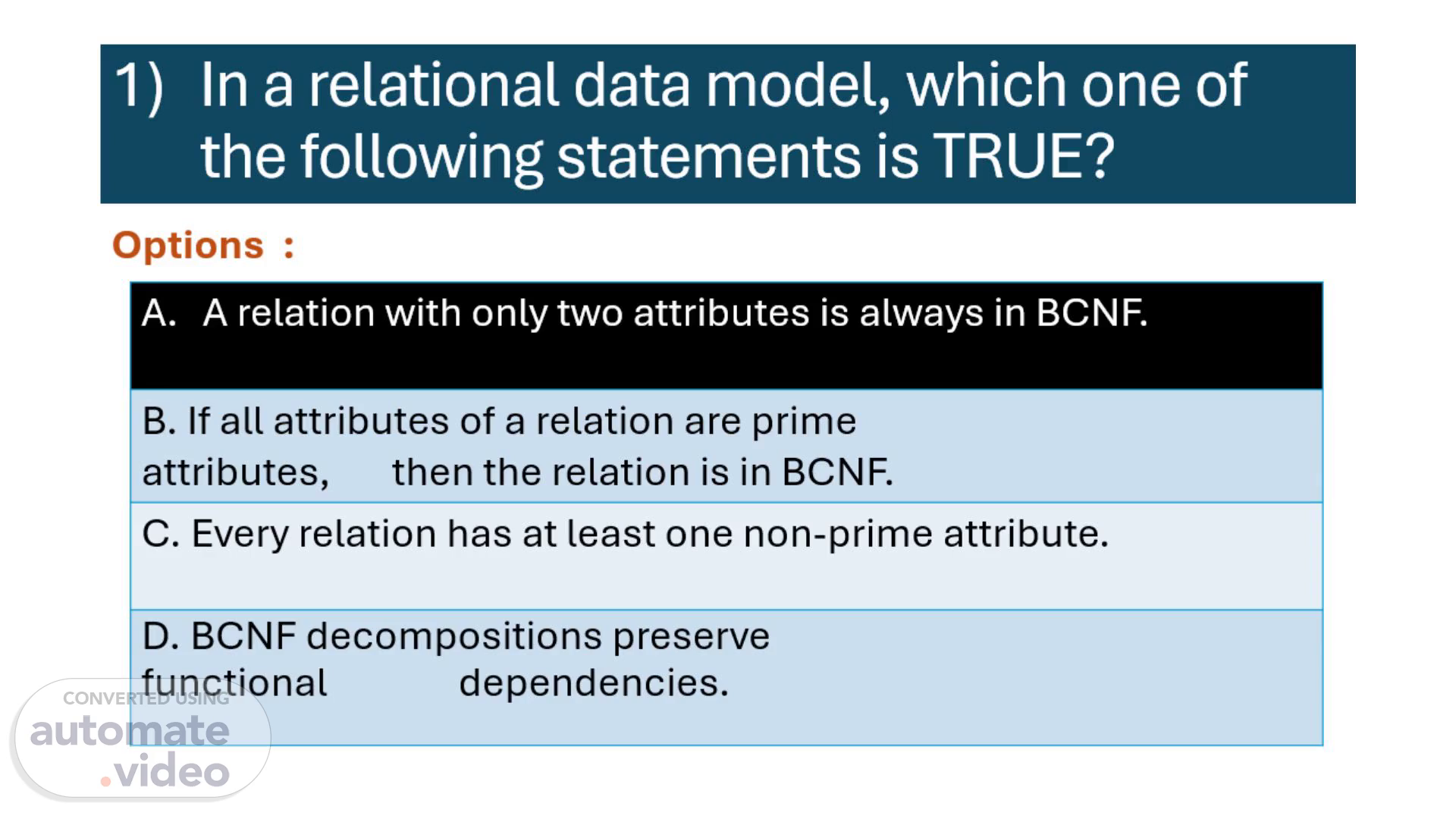
[Audio] The first question is In a relational data model, which one of the following statements is TRUE? And the options are : A relation with only two attributes is always in BCNF. B. If all attributes of a relation are prime attributes, then the relation is in BCNF. C. Every relation has at least one non-prime attribute. D. BCNF decompositions preserve functional dependencies. And the correct option is A..
Scene 2 (28s)
[Audio] Relation with 2 attributes always in BCNF R(AB) => BCNF => BCNF => BCNF => BCNF If all prime attributes than relation always in 3NF but may not BCNF. Not mandatory of atleast one non-prime attribute in RDBMS table. Not every relation can decompose into BCNF with dependency preserving..
Scene 3 (57s)
[Audio] The next question is Consider the following three relations in a relational database. Employee (egg, Name), Brand (bld , bName), Own (egg,bld) Which of the following relational algebra expressions return the set of elds who own all the brands? And the options are here. And the options are.
Scene 4 (1m 19s)
[Audio] Option a It results in "eid's which own every brand of the brand relation." and option b Expansion and division using basic operators.
Scene 5 (1m 31s)
[Audio] The next question is Consider a relation R(A, B, C, D, E) with the following three functional dependencies. AB -> C; BC -> D; C -> E; The number of super keys in the relation R is moving towards the question is Consider a relation R(A, B, C, D, E) with the following three functional dependencies. AB -> C; BC -> D; C -> E; The number of super keys in the relation R is and here AB will be the candidate key and there are 8 super keys in the relation R.
Scene 6 (2m 7s)
[Audio] The next is Consider the relational database with the following four schemas and their respective instances. Student( sNo, sName, dNo) Dept( dNo, dName) Course(cNo, cName, dNo) Register( sNo, cNo) lets look into the student table, department table, course table, register table.
Scene 7 (2m 25s)
[Audio] The given query is SELECT * FROM Student AS S WHERE NOT EXIST (SELECT cNo FROM Course WHERE dNo = "D01" EXCEPT SELECT cNo FROM Register WHERE sNO = S.sNo) the number of rows returned by the above sql query is explation is Given SQL query retrieves student records who register for all courses of dno =D01. Course id's and dept D01 are Result students who register and all C11 C12 courses which are S01, S04 students records..
Scene 8 (3m 0s)
[Audio] The next question is Consider a relation R(A, B, C, D, E) with the following three functional dependencies. AB -> C; BC -> D; C -> E; The number of super keys in the relation R is explationation is Finding the key of the relation, Compute closure of attribute, + = + = + = Only one candidate key is possible for given relation = AB Superkeys of the relation = 2^Total number attributes in relations - Total number of attributes in each key. Superkeys of the relation = 2^5-2 Superkeys of the relation = 2^3 = 8 keys So the Number of super keys is 8..
Scene 9 (3m 50s)
[Audio] This question asks for the meaning of arity and the options are A. Number of entries in the table B. Number of samples in the table C. Number of attribute in the table D. Number of records in the table and the correct answer is option C . Number of attribute in the table.