Scene 1 (0s)
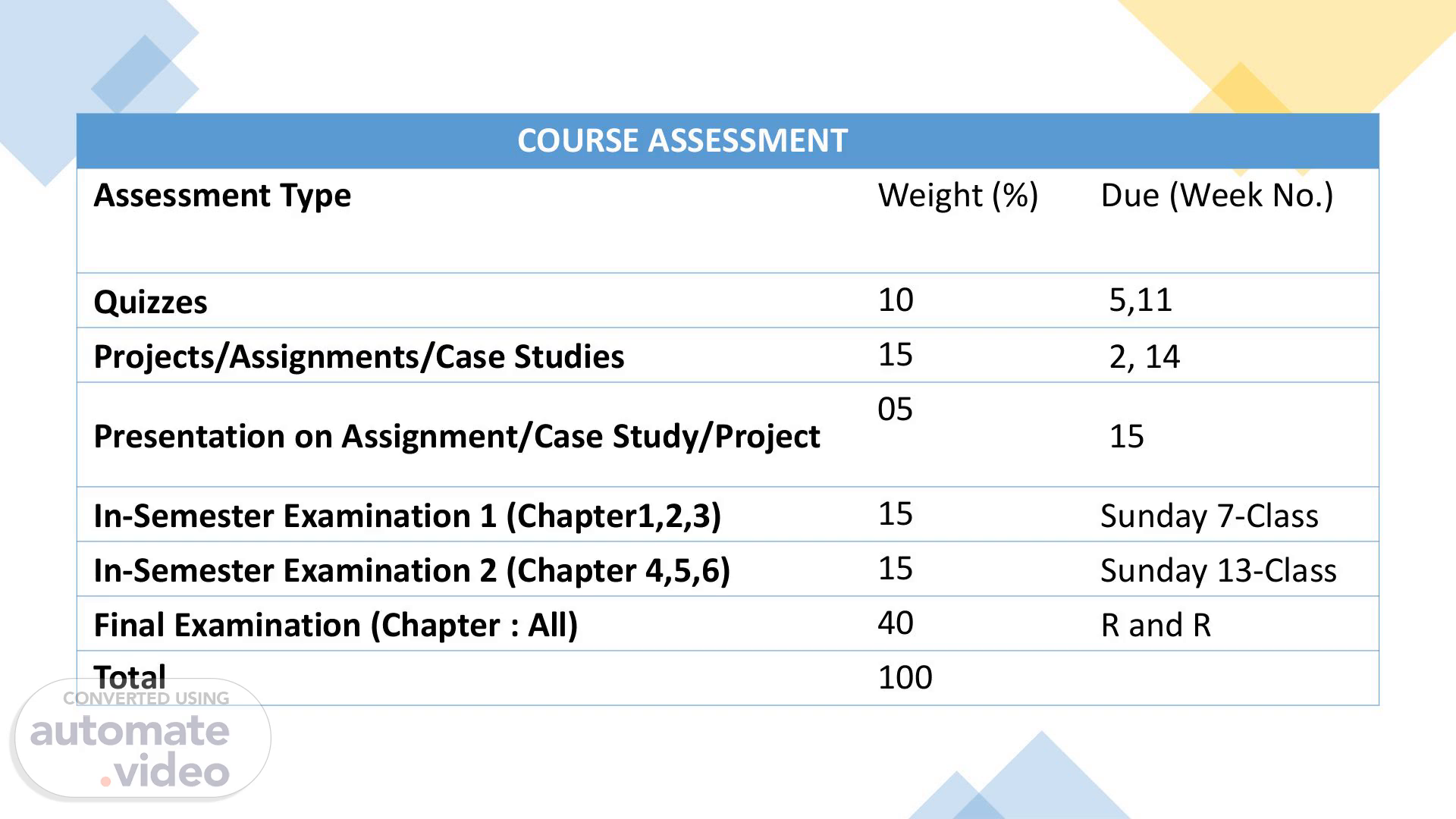
COURSE ASSESSMENT Assessment Type Weight (%) Due (Week No.) Quizzes 10 5,11 Projects/Assignments/Case Studies 15 2, 14 Presentation on Assignment/Case Study/Project 05 15 In-Semester Examination 1 (Chapter1,2,3) 15 Sunday 7-Class In-Semester Examination 2 (Chapter 4,5,6) 15 Sunday 13-Class Final Examination (Chapter : All) 40 R and R Total 100.
Scene 2 (15s)
Chapter 1 Islamic Banking- Theoretical Foundation.
Scene 3 (21s)
Why Are Islam and Islamic Finance Necessary? • Question: • Why does Islam emphasize social responsibility and justice in financial matters, and how does this lead to the necessity of Islamic finance? • Qur’an Verse: • "And of everything We have created pairs, that you may remember (the Grace of Allah)." • — Surah Adh-Dhariyat (51:49).
Scene 4 (38s)
• The Concept of Pairs in the World • The world is created in pairs—not only in physical forms like male and female but also in abstract concepts that define justice and morality. These opposing pairs highlight the balance Islam promotes in every aspect of life, including finance. • Positive Trait (Guidance) Negative Trait (Misguidance) • Truth (Haqq) Falsehood (Batil) • Justice (Adl) Injustice (Dhulm) • Mercy (Rahma) Oppression (Zulm) • Trust (Amanah) Betrayal (Khiyanah) • Modesty (Haya) Shamelessness (Fahsha) • Generosity (Sakhawa) Greed (Bukhl) • Ethical Finance (Halal) Exploitative Finance (Riba) • Man ,women , Jannah , jahunm.
Scene 5 (1m 0s)
• The Goal of Evil vs. The Role of Islam • The ultimate goal of self-serving systems is to secure their own interests rather than promote social responsibility. They use financial power to exploit the weak, benefiting a few at the expense of many. This is why Islam has set principles to protect society, ensuring justice and care for all. • Islamic finance is a direct result of these principles. It is not just a financial system; it is a moral and ethical framework designed to: • Prevent exploitation (Riba, Gharar, Maysir) • Ensure fairness and equity • Protect the vulnerable from economic oppression • Promote social welfare and economic justice • For these reasons, Islamic financial institutions are essential. They uphold these principles, ensuring that financial systems serve humanity rather than enslaving them..
Scene 6 (1m 33s)
•📢 Riba: A Blessing or a Trap? •If it’s bad—why does it still exist? 🤔 •Does it help the rich get richer while the poor struggle? •Is it ethical to profit from someone’s hardship? •Why do major religions warn against it? •Let’s uncover the truth behind riba (interest)—is it just a financial tool, or a system of exploitation?.
Scene 7 (1m 49s)
Activity: Choosing a Bank Wisely • 🤔 Activity Prompt: Imagine you are about to open a bank account or take a loan. What factors would influence your decision?“ • Discussion with Hints • Think critically • Interest Rates – Would you prefer a bank that charges high or low interest? • Ethical Considerations – Should a bank operate based on fairness and justice? • Transparency & Risk-Sharing – Do you want a bank that shares risks and profits with customers? • Social Impact – Should banks contribute to society and help those in need? Factors Conventional Banking Islamic Banking Interest (Riba) Yes, charged on loans & deposits No, profits shared instead Risk- Sharing Bank takes little risk Bank shares risk with customers Ethical Focus Profit-driven Justice, fairness, and social responsibility.
Scene 8 (2m 16s)
Activity: Choosing a Bank Wisely 🤔 Imagine you are about to open a savings account to earn profit. What factors would influence your decision? • Profit vs. Interest – Do you want to earn interest (riba) or profit through ethical investments? • Risk Involvement – Would you prefer a fixed return, or one based on profit-sharing? • Ethical Considerations – Does it matter how the bank invests your money (e.g., ethical vs. non-ethical industries)? • Transparency & Security – Do you value knowing where and how your money is used? • Religious or Ethical Beliefs – Do your values align with conventional or Islamic banking principles? Factors Conventional Savings Account Islamic Savings Account Interest (Riba) Fixed interest earnings Profit - sharing model (Mudarabah) Risk & Returns Low risk, guaranteed returns Profits based on bank’s investment success Ethical Investment No restriction on investments Funds invested in ethical, Sharia - compliant industries Transparency Limited transparency High transparency in fund usage.
Scene 9 (2m 43s)
Religious perspective on Ribbah • 📖 Islam: The Quran warns: "Allah has permitted trade and forbidden riba." (Surah Al-Baqarah 2:275) It emphasizes fairness and justice, discouraging exploitation of the needy. • 📖 Christianity: The Bible states: “Do not charge your brother interest, whether on money or food or anything else that may earn interest.” (Deuteronomy 23:19) Christian teachings also stress compassion and fairness in financial dealings. • 📖 Judaism: The Torah teaches: “If you lend money to My people, to the poor among you, do not act as a creditor; do not take interest from them.” (Exodus 22:25) Jewish ethics align with protecting the vulnerable from financial oppression.
Scene 10 (3m 11s)
• . 📖 Hinduism : Hindu scriptures promote dharma (righteousness) and discourage unjust financial practices . The Manusmriti (Chapter 11 , Verse 62 ) warns against wealth gained through exploitation . • 📖 Buddhism : The concept of Right Livelihood in the Noble Eightfold Path teaches that wealth should be earned ethically without harming others . Exploitative lending contradicts this principle . • Why do many religious traditions discourage charging interest? • Why Conventional Banking Still Exists 1.Economic Necessity – In modern economies, credit and loans are essential for business, home purchases, and infrastructure development. Interest-based banking became a practical tool for economic growth. 2.Legal & Cultural Adaptations – Many societies evolved to accept interest-based banking as long as it was regulated to prevent exploitation. 3.Alternative Financial Models – Some religious groups developed alternatives, such as: 1. Islamic Banking – Uses profit-sharing (mudaraba), cost-plus financing (murabaha), and leasing (ijara) instead of interest. 2. Ethical & Cooperative Banks – Some Christian and Jewish groups promote interest-free lending through community-based finance..
Scene 11 (3m 44s)
Questions • How does conventional banking increase the financial burden on the poor? • What ethical financial alternatives exist today?.
Scene 12 (3m 53s)
The Origins of Conventional Banking • Key Name: Giovanni di Bicci de' Medici & the Medici Bank • Founded: 1397 in Florence, Italy • Details: • The Medici Bank is widely recognized as one of the earliest and most influential modern banking institutions. • Founded by Giovanni di Bicci de' Medici—a member of a powerful Florentine family—this bank pioneered practices such as accepting deposits, issuing loans, and facilitating currency exchange. • Although early Christian teachings (prevailing in medieval Europe) originally condemned usury (excessive interest), evolving interpretations allowed the practice to develop. Thus, what began in a predominantly Christian context became the foundation of the conventional interest-based banking system used worldwide today. • Other historical names (for context): • Fugger Family (Germany): Later, during the Renaissance, banking families like the Fuggers built upon these early practices, further advancing European finance. • Rothschild Family (Europe): In the 18th and 19th centuries, this family became synonymous with modern international finance, again in a Christian‐influenced context..