Microsoft PowerPoint - SM-313 Bloodborne Pathogens - Compatibility Mode
Scene 1 (0s)
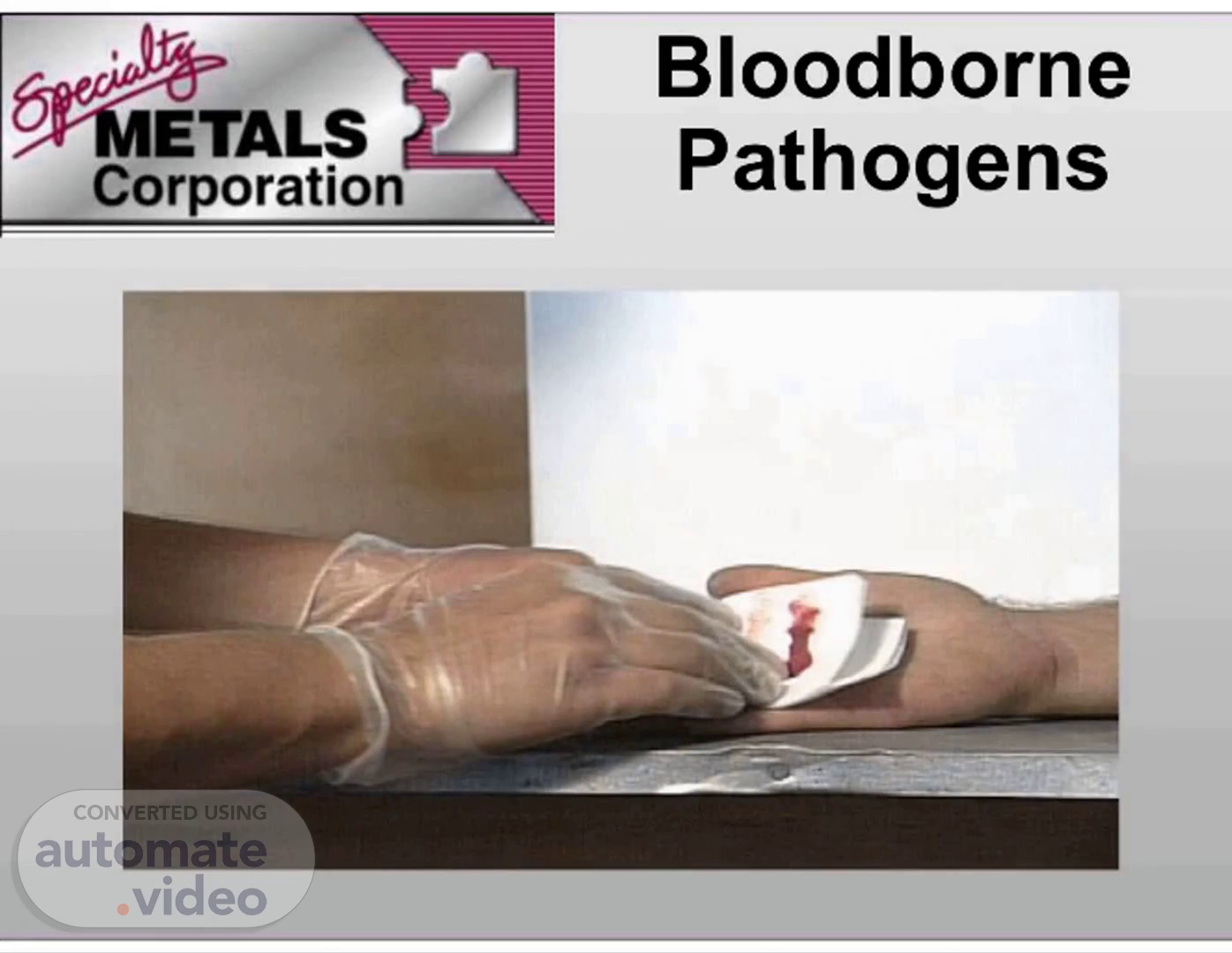
Bloodborne Pathogens. Bloodborne Pathogens.
Scene 2 (5s)
Bloodborne Pathogen Standard Required by OSHA (29 CFR 1910.1030) Applies to employees in all industries who may be exposed to blood or other potentially infectious materials.
Scene 3 (23s)
What are Bloodborne Pathogens? Microorganisms such as viruses or bacteria that are present in human blood and can cause diseases in humans – Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) – Hepatitis B Virus (HBV) – Hepatitis C Virus (HCV).
Scene 4 (43s)
[Audio] Human Immunodeficiency Virus (H-I-V--) The virus which causes A-I-D-S Devastates the body’s immune system ~1 million persons living with HIV/AIDS in U S ; 45000 new cases in 2000 Symptoms: flu like illness, weakness, diarrhea, weight loss. Signs of illness may not be present for years A-I-D-S is chronic and fatal.
Scene 5 (1m 10s)
[Audio] Hepatitis B (H-B-V--) Attacks the liver Survives in dried blood for up to 1 week at room temperature 300000 new infections annually; 1.4% result in death Symptoms: fatigue, nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, anorexia Can be chronic and fatal.
Scene 6 (1m 30s)
[Audio] Hepatitis C (H-C-V--) Can lead to chronic hepatitis, cirrhosis and liver cancer 4 million infected in U S – Only 25% diagnosed Can be chronic and fatal 8000-10000 deaths annually No effective vaccine exists.
Scene 7 (1m 50s)
[Audio] Potentially Infectious Materials Blood Human bodily fluids such as: – Semen, vaginal secretions, lung fluid Any bodily fluid containing visible blood Any bodily fluid that cannot be identified.
Scene 8 (2m 9s)
[Audio] How Are They Transmitted? Puncture wounds caused by sharp objects Infectious materials contacting open wounds, cuts, or broken or damaged skin Infectious materials contacting mucous membranes of eyes, nose and mouth.
Scene 9 (2m 24s)
[Audio] Possible Exposure Incidents During an industrial accident While administering First Aid During post accident clean up When performing routine maintenance or janitorial work.
Scene 10 (2m 35s)
[Audio] Exposure Control Plan Universal precautions Engineering controls Work practice controls Post exposure follow up.
Scene 11 (2m 45s)
[Audio] Universal Precautions Treat all human blood and bodily fluids as if they are infected with H-I-V--, H-B-V--, H-C-V and other bloodborne pathogens..
Scene 12 (2m 57s)
[Audio] Engineering Controls & Work Practice Controls Work Practice Controls Engineering Controls – Personal protective – Handwashing equipment (P-P-E--) facilities – First aid response – Biohazard waste bags – Spill clean up – Laundry – Waste disposal – Exposure response.
Scene 13 (3m 16s)
[Audio] Personal Protective Equipment First line of defense Examples and uses Limitations Rules: – Remove before leaving work area – Wash hands after removing – Properly dispose of contaminated P-P-E.
Scene 14 (3m 31s)
[Audio] First Aid Response Adopt Universal Precautions Encourage self care Use PPE Avoid applying pressure without barrier.
Scene 15 (3m 40s)
[Audio] Housekeeping: Spill Clean up Use PPE & Universal Precautions Cover spill or area with paper towel or rags Pour disinfectant solution over towels or rags Leave for at least 10 minutes Place materials in appropriate container Arrange for pick up and disposal.
Scene 16 (4m 1s)
[Audio] Housekeeping: Waste Disposal Use P-P-E when handling Leak proof containers Proper labeling – Labels – Red Bags or Containers Drop off sites.
Scene 17 (4m 12s)
[Audio] Housekeeping: Contaminated Laundry Laundry soiled with blood or opim Use P-P-E Handle as little as possible Pre soak all contaminated clothing If blood or opim gets on clothing, remove and thoroughly wash with detergent asap.
Scene 18 (4m 29s)
[Audio] Exposure Incident Response Contact with skin: wash exposed areas with antibacterial soap and running water Contact with eyes or mucous membranes: flush affected area with running water for at least 15 minutes Contact with clothing: remove contaminated clothing, wash underlying skin Report exposure to supervisor immediately.
Scene 19 (4m 52s)
[Audio] Post Exposure Evaluation Confidential medical evaluation and follow up after exposure incident – Identify and document source and circumstances of exposure – Test source individual’s blood for HIV/HBV – Provide blood sample Healthcare professional’s written opinion.
Scene 20 (5m 8s)
[Audio] Hepatitis B Vaccination Made available to all employees at risk for occupational exposure prior to initial job assignment Made available after exposure incident.
Scene 21 (5m 23s)
[Audio] Summary Bloodborne Pathogens Transmission Potentially infectious materials Exposure incidents Prevention – Universal Precautions – P-P-E Response.
Scene 22 (5m 36s)
[Audio] Questions Please feel free to ask any questions about the material we’ve covered.