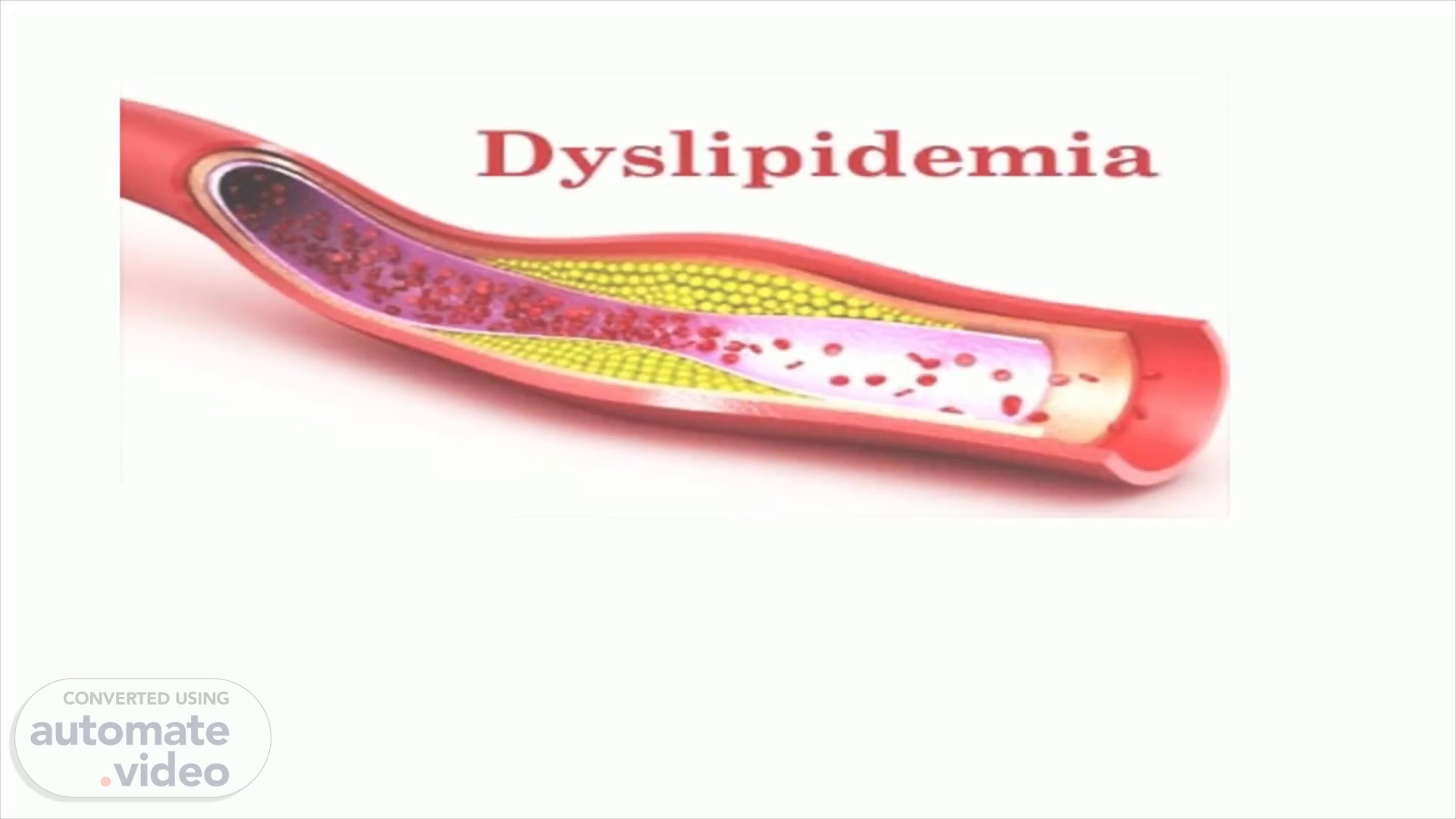
Scene 1 (0s)
By Asmaa badawy. Dyslipiderrnia.
Scene 2 (41s)
Lipoproteins. Lipid Protein Lipoprotein.
Scene 3 (1m 24s)
Lipoprotein = lipid transport.
Scene 4 (1m 31s)
Causes of Hyperlipidemia Lifestyle Diabetes Mellitus Kidney disease Pregnancy Hypothyroidism Genetic Alcohol Dyslipidemia Drugs- Thiazides, Cyclosporin, Glucocorticoids, Beta Blockers..
Scene 5 (2m 25s)
Protein Phospholipid Cholesterol Triglyceride A. A lipoprotein 0000 0 Chylomicron — VI-DL HDL B. The variety Of lipoproteins Blood Lipids Serum Triglycerides • VLDL • CHYLOMICRONS Serum Cholesterol • LDL (Bad, 77.5%) • HDL (Good, 17.5%) IDL (Neutral, 5%).
Scene 6 (3m 17s)
1-chylomicron mainly T.G carry lipid from intestine to liver 2-VLDL mainly T.G from liver to blood 3-ILDL half cholesterol half T.G 4-LDL mainly cholesterol bad cholesterol 5-HDL from tissues to liver good cholesterol.
Scene 7 (4m 44s)
6/1/2022. Life Cycle of Cholesterol-carrying LIPOPROTEINS Liver produces LIPOPROTEINS LDL Lipoprotein Molecule Triglyceride (fat) VLDL fat ce Ils TRIGLYCERIDE Muscle burn TRIGLYCERIDE.
Scene 9 (7m 7s)
0.95 1 .006 1 .02 1 .06 1.10 1.20 HDL o 5 o 10 IDL LDL 20 VLDL 40 Diameter, nm Chylomicron remnants Chylomicron 60 80 1 ooo.
Scene 10 (7m 12s)
Antihyperlipedemic drugs. Hyperlipidemia SINGLE USE ONLY.
Scene 11 (8m 5s)
Classification. Statins Niacin Fibrates Bile acid resins, Ezetimibe.
Scene 12 (8m 13s)
BILE ACID-BINDING RESINS (CHOLESTYRAMINE) 1-Bind to bile acids in the intestine decrease cholesterol and T.G absorption 2-prevent their absorption and . preventing the recycling of bile acids, bile acid-binding resins divert hepatic cholesterol to synthesis of new bile acids, thereby reducing the amount of cholesterol..
Scene 13 (9m 43s)
Mechanism of action. ÙتÙجة بØØ« اÙصÙر ع٠âªbile binnding resinâ¬â.
Scene 14 (10m 0s)
Side effect 1-GIT disturbance (steatorrhea) 2-decrease absorption of fat soluble vitamins 3-cholesterol gall stones.
Scene 15 (10m 47s)
EZETIMIBE.
Scene 16 (11m 7s)
Mechanism of action Selective inhibition of cholesterol absorption both 1-exogenous (dietary ) 2-endogenous (biliary).
Scene 18 (11m 20s)
Preparations (HMG CO A Reductase inhibitors) atorvastatin, simvastatin.
Scene 19 (11m 34s)
Mechanism of action Inhibition of HMG-co A reductase decrease so, inhibit synthesis of cholesterol in liver.
Scene 20 (12m 5s)
Side effects of statins MUSCLE Muscle pain Rhabdomyolysis LIVER Liver failure.
Scene 21 (12m 46s)
ÙتÙجة بØØ« اÙصÙر ع٠âªniacin hypolipidemicâ¬â.
Scene 22 (12m 57s)
Mechanism of action ( agonist to nicotinic acid VIT B3 ) Inhibition of lipolysis decrease FFA production decrease T.G synthesis in liver.
Scene 23 (13m 44s)
S.E OF NIACIN 1-increase P.G vasodilators hypotension ,flushing(can be managed by NSAIDS ) 2- increase histamine release in GIT HCL secretion ,colic.
Scene 24 (14m 36s)
صÙرة ذات صÙØ©.
Scene 25 (14m 42s)
Mechanism of action of fibrates Agonist of PPAR nuclear receptor (activation of lipoprotein lipase) metabolism of T.G.
Scene 26 (15m 49s)
26. 1- GIT disturbance 2-cholesterol gall stones 3-liver enzymes elevation 4-myopathy.
Scene 27 (16m 42s)
COMBINATION THERAPY: Drug combinations are often required to achieve the maxi- mum lowering effect with minimum toxicity Certain drug combinations provide advantages whereas others present specific challenges..
Scene 28 (18m 1s)
Because resins interfere with the absorption of certain HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors these must be given at least 1 h before or 4 h after the resins. The combination of reductase inhibitors (statin) with fibrates increases the risk of myopathy..
Scene 29 (18m 57s)
1-statin,resin (time interval) 2-statin ,niacin 3-niacin,resin Good combinations 1-fibrate,resin both increase gall stones 2-statin,fibrate both hepatotoxic ,myopathy Bad combinations.
Scene 31 (20m 55s)
صÙرة ذات صÙØ©.